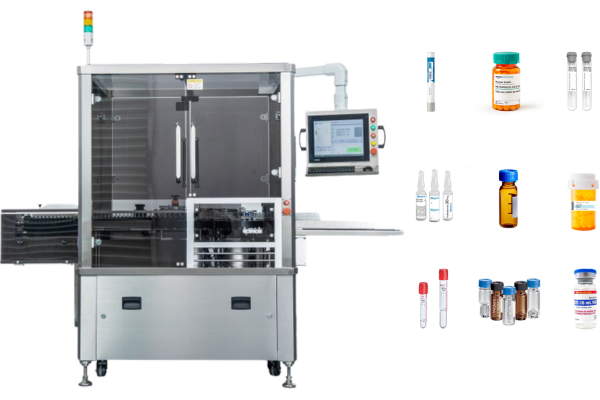
In modern production environments, a reject system is indispensable for maintaining high standards of product quality and operational efficiency. This system, typically integrated into assembly lines, automatically identifies and removes defective or contaminated products that fail to meet quality specifications.
Understanding the mechanisms, applications, and benefits of these systems is crucial for industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to food and beverage, where compliance with safety standards is mandatory.
Overview of rejection systems
A reject system functions by detecting and removing products that do not adhere to the set quality criteria. These systems are equipped with various sensors and detection mechanisms that scan each item for defects.
Upon detection, the system activates a mechanism to discard the defective item, ensuring that only products meeting the quality standards proceed further in the production lines.

Types of rejection systems
Conveyor reject mechanisms are essential for maintaining product quality and efficiency in production lines. Here are some common types:
- Mechanical rejection: Utilizes physical devices like pushers or arms to remove defective products from the conveyor belt.
- Pneumatic pusher: One of the most popular conveyor reject mechanisms, the pneumatic pusher efficiently removes items by pushing them off the conveyor belt into a designated reject bin.
- Pneumatic rejection: Employs compressed air to gently blow faulty items off the line, ideal for delicate products.
- Air blast: This mechanism uses a nozzle attached to the outfeed conveyor to deliver a burst of air that efficiently removes contaminated products from the conveyor belt without interrupting the production flow, making it particularly suitable for lightweight, packaged items.
- Optoelectronic rejection: Uses cameras and light sensors to identify inconsistencies in products and initiates rejection through precise mechanical or pneumatic mechanisms.
Applications in various industries and production lines
- Food and beverage: Ensure the safety and quality of food products by removing those with improper seals, incorrect weights, or visual defects. Reject mechanisms efficiently handle different types and weights of packaged products, ensuring compliance with quality specifications while maintaining production efficiency.
- Pharmaceuticals: Critical for removing products that could compromise patient safety, such as vials with incorrect labels or missing caps. Effective rejection systems are essential for managing non-conforming products, ensuring compliance with various safety regulations, and minimizing waste.
- Electronics: Detects and rejects components with physical damage or assembly flaws, ensuring the reliability of electronic devices.

Technical requirements for rejection systems and conveyor reject mechanisms
- Accuracy: High precision in detecting defects is crucial to avoid false rejections and ensure no defective product is overlooked.
- Speed: Must keep up with the production line speeds without causing bottlenecks. Understanding the production line’s belt speed is essential in selecting the appropriate reject mechanism for effective contaminant removal.
- Reliability: Should perform consistently over long periods with minimal maintenance. Maintaining continuous product flow is vital to ensure that the production process remains uninterrupted while effectively removing contaminated products.
Integration and optimization
Seamless integration
Rejection systems must be integrated into existing production lines without significant disruptions. A well-designed reject conveyor can efficiently remove defective or unwanted products, ensuring that only compliant items reach the marketplace.
Data-driven optimization
Leveraging production data to refine rejection algorithms and settings can enhance the system’s effectiveness and reduce wastage. Various reject systems, including pneumatic air blasts or physical reject arms, direct contaminated or unwanted items into a designated reject bin for proper disposal, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and minimizing production disruption.
Challenges faced by rejection systems and rejected products
- High-Speed production lines: Maintaining accuracy at high speeds is a significant challenge.
- Product diversity: Adapting to different product types and sizes on the same production line can complicate the setup and calibration of rejection systems. The integration of metal detectors can help identify contaminants in various products, working in conjunction with retracting reject conveyors to automate the rejection process.
- Environmental factors: Dust, humidity, and temperature variations can affect the sensitivity and accuracy of sensors used in rejection systems. The use of plastic components, particularly FDA-approved belting, ensures hygiene and safety in guiding products along the conveyor line.

Future trends
- Smart technologies: Incorporation of AI and machine learning to predict and automatically adjust to changes in product specifications or production conditions. Advanced X-ray systems play a crucial role in automated reject systems by enhancing quality assurance, identifying non-conformant products, and minimizing false reject rates.
- Sustainability: Advances in technology that allow for energy-efficient and less wasteful rejection systems.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of a reject system in managing rejected products on a production line directly correlates with enhanced product quality, reduced waste, and improved consumer satisfaction. As technology evolves, these systems are becoming more integrated and intelligent, capable of handling higher throughput with greater precision.
For manufacturers, investing in advanced rejection systems means stepping towards more automated, efficient, and error-free production processes, ensuring that only products meeting the strictest quality standards reach the market.
Our pharmaceutical labeling machines (e.g. vial labeling machines, syringe labeling machines, tube labeling machines, etc.) All use rejection systems to increase productivity for screening the right products ……