Drug-making process should use pharmaceutical equipment. They help speed up different production tasks.
Solid dose and liquid drugs both need special machines. These machines handle each step of making medicine. Next, you will learn about the different machines used to make drugs.
Pharmaceutical processing equipment and their functions
Agitators
Mix liquids, help with reactions, and move heat or cold.

Blowers
Help recover solvents and support evaporation in making medicine.

Boilers
Make steam by heating water for cleaning and heating tasks.

Capsule equipment
Fill, polish, and sort capsules for correct doses.

Capsule and tablet printers
Print drug names and dosages on pills.

Centrifuges
Separate liquids or remove liquids from solids for purity.

Chillers
Quickly cool things down during medicine making.

Coaters
Add coatings to tablets or capsules for taste and look.
Cooling towers
Cool liquids or steam for controlled temperatures.

Dryers and granulators
Turn liquids into powders or granules.

Heat exchangers
Transfer heat between different materials.

High-pressure homogenizers
Make particles smaller and break cells.

Inspection machines
Check products for quality as they move.

Metal detectors
Find and remove metal bits from products.

Mixers
Blend ingredients and make them uniform.

Ovens
Provide heat to dry and sterilize products.

Pulverizers / Cone mills
Reduce the size of granules.

Tablet presses
Compress powders into tablets of exact sizes.

Tablet deduster
Removes dust and smooths tablet surfaces.

Sifters
Sort powders and granules by size.
Spray coating machines
Apply coatings to powders for better stability.

Tanks
Store and handle liquids used in manufacturing.

Primary and secondary packaging equipment and their functions
Blister packers
Package tablets and capsules into blister packs.

Deblistering machines
Recover contents for reuse or repackaging.
Bottling and filling lines
Fill bottles with liquids or tablets.

Cappers
Place caps securely on filled bottles and containers.
Cartoners
Fill medicine boxes, fold leaflets, and seal boxes.
Counters
Count and verify capsules and tablets accurately.
Induction sealers
Seal aluminum foil onto bottle mouths.
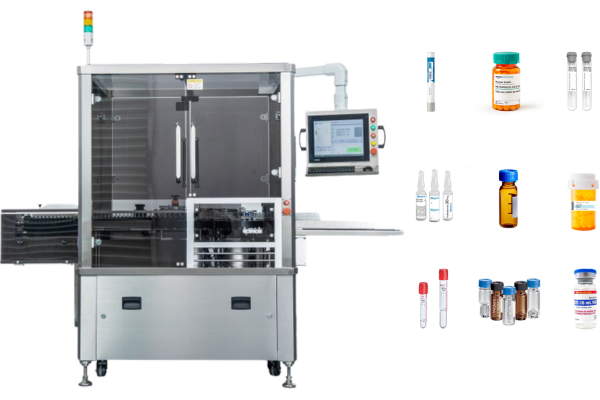
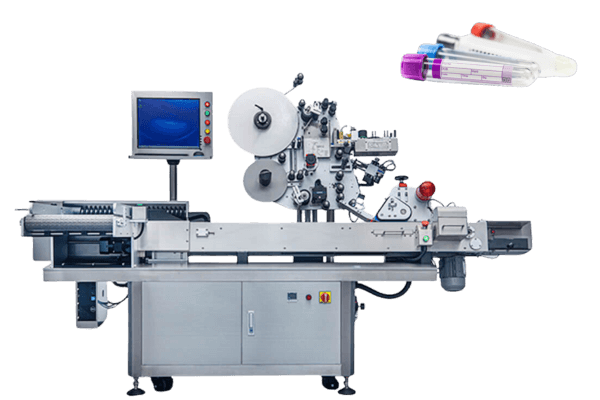
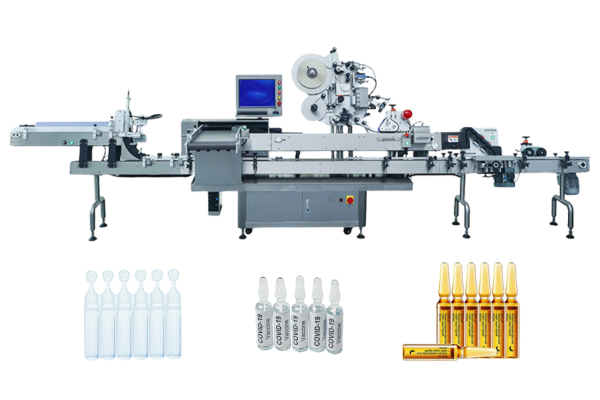
Labeling equipment
Attach or print labels on boxes, bottles, and tubes. Viallabeller offers horizontal labeling solutions and wrap-around labeling solutions.

Tube fillers
Fill and seal tubes with ointments and gels.
Sterilization and automatic visual inspection equipment
Autoclaves
Sterilize equipment and containers with high-pressure steam.
Sterile filling machines
Fill sterile products into containers under clean conditions.
Tunnel sterilizers
Sterilize containers and packaging with heat or chemicals.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical equipment supports precise manufacturing processes. It helps keep product quality and safety. Optimizing production in pharmaceutical manufacturing improves product quality and efficiency.