Serialized packages have become a cornerstone of modern pharmaceutical packaging, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and enhancing the traceability and safety of drugs through serialization in pharmaceutical packaging. Serialization involves assigning a unique identifier to each product, which is then tracked throughout the supply chain.
This process not only helps in combating counterfeit drugs but also facilitates efficient recall processes and inventory management.
Components of pharmaceutical serialization packages
To fully understand serialized packages in the pharmaceutical industry, it’s essential to examine their key components:
- Barcodes and serial numbers: The backbone of serialization lies in the generation of unique serial numbers and barcodes. These identifiers, such as QR codes, Data Matrix codes, and Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs), are printed on the packaging and stored in a centralized database. This ensures each package can be uniquely identified and tracked from the manufacturing facility to the end consumer.
- Data management systems: Efficient data management systems are crucial for handling the vast amounts of data generated by serialization. These systems manage the generation, distribution, and storage of serial numbers, ensuring data integrity and security. They also provide the infrastructure for tracking and tracing products across the supply chain.
- Labels and packaging materials: The selection of appropriate labels and packaging materials is vital to the success of serialized packages. Labels must be durable and adhere well to various packaging surfaces while maintaining the readability of the barcodes, serial numbers, and expiration dates throughout the product’s lifecycle. The packaging materials should support the overall integrity of serialized information.

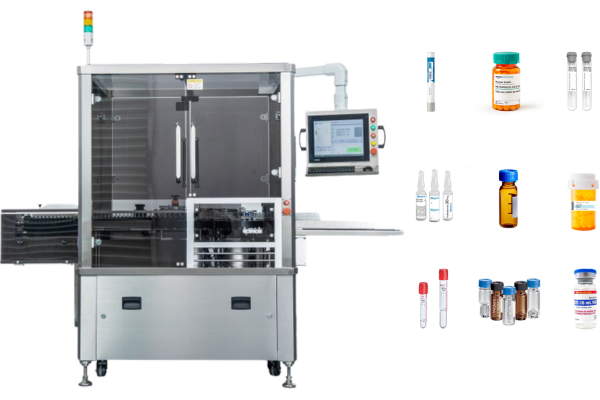
Role of labeling machines in the pharmaceutical industry serialized packages
Labeling machines play a pivotal role in the implementation of serialized packaging, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in the application of labels.
- Printing and applying labels Labeling machines are responsible for printing the serialized data onto labels and precisely applying these labels to the packaging. Labeling machines are integrated into the production line to ensure seamless printing and application of serialized data onto labels. High-precision labeling ensures that the barcodes and serial numbers remain legible and scannable, which is essential for effective tracking.

- Automation and efficiency: Modern labeling machines are equipped with advanced automation capabilities, which significantly boost production efficiency. Automation minimizes manual intervention, reducing the risk of errors and increasing throughput. This is particularly important in high-volume pharmaceutical manufacturing environments.
- Quality control and verification: Ensuring the quality and accuracy of the labels is critical. Labeling machines often include verification systems that check the labels after application to ensure they meet quality standards. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of serialized packages and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Compatibility and flexibility: Labeling machines must be versatile enough to handle various packaging sizes and shapes. They should also support different types of labels, including those used in secondary packaging, such as cartons, to meet diverse product requirements. Flexibility in label materials and sizes is essential for adapting to different pharmaceutical products.
Our pharmaceutical labeling machines can meet the above needs. We also have a series of pharmaceutical labeling solutions, such as medicine carton labeling solutions and syringe labeling solutions…
Steps to implement serialized packages in the pharmaceutical supply chain
Implementing serialized packaging involves several key steps:
- Planning and design: The first step is to conduct a thorough needs analysis and design a serialization system that meets those needs. This includes selecting appropriate labeling machines and data management systems that can handle the serialization processes efficiently.
- Installation and commissioning: Once the system design is finalized, the next step is to install and configure the labeling machines and integrate the data management systems. Proper installation and commissioning of serialization solutions are crucial to ensure the system operates correctly from the start.
- Training and operation: Training personnel on the operation and maintenance of the serialization system is essential. This includes providing detailed operating procedures and maintenance guidelines to ensure the system runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Testing and validation: Before full-scale production, the serialization system must be thoroughly tested and validated. This step ensures that all components function correctly and that the system complies with regulatory requirements.
- Operation and monitoring: After validation, the system performs regular operations. Continuous monitoring and periodic maintenance are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and efficiency. Any issues that arise should be promptly addressed to minimize downtime and maintain productivity.

Challenges and solutions for counterfeit drugs
Implementing serialized packages in the pharmaceutical industry comes with several challenges, but solutions are available to address these issues:
Technical challenges: Integrating new serialization systems with existing infrastructure can be technically challenging. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data exchange between systems is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the entire supply chain. Robust data security measures must also be in place to protect sensitive information.
Operational challenges: Training personnel and providing ongoing technical support are essential for pharmaceutical companies to overcome operational challenges. Effective training programs and accessible support resources help ensure that employees are capable of managing and troubleshooting the serialization system.
Conclusion
Serialized packages are an essential aspect of modern pharmaceutical packaging, enhancing drug safety, traceability, and regulatory compliance, which ultimately helps improve patient safety. The role of labeling machines in this process is critical, providing the precision and efficiency needed to apply unique identifiers to each product.
As the industry continues to evolve, the importance of pharma serialization will only grow, driving further innovations in labeling technology and data management systems.