How do conveyor belts work? A belt conveying system is used to systematically carry and transport materials, usually in an industrial or controlled environment. Conveyor belts have been around for a long time and are known for saving energy and increasing efficiency. Let’s take a look at how conveyor belts operate and why they continue to be reliable over the years.
The working principle of conveyor belts
To understand how conveyor belt work, it is essential to know that a conveyor belt operates by using two motorized pulleys that loop over a long stretch of thick, durable material. When the motors in the pulleys run at the same speed and spin in the same direction, the belt moves smoothly between the two.
If objects are particularly heavy, and bulky, or need to be transported over a long distance, rollers can be added on the sides of the conveyor belt for extra support, ensuring efficient and reliable transportation.
Parts of a conveyor belt system
A conveyor belt system is designed to transport materials efficiently. While there are various types of conveyor systems, many use a belt to carry materials. Some systems may use only rollers or wheels for flexible movement, but most rely on a frame with a belt and support rollers.
Belt conveyors come in various types, such as cleated and modular belt conveyors, each designed for specific processes and applications.
All conveyor systems have three main components: the aluminum profile, the driving unit, and the extremity unit.
The aluminum profile includes the frame, belt, and supports. Systems with a belt are usually powered by a motor, but some can use gravity or manual force. Motorized belts are more reliable and efficient for industrial use. The driving unit includes the motor bracket, electrical drive, and counter bearings.
The extremity unit has pulleys and clamping straps. Additional stands or lateral guides may be needed depending on the system’s function.
Parts of a conveyor belt system include:
- The frame: Holds all parts together for safe operation.
- The belt: A durable material that transports items from one place to another.
- The conveyor belt support: Rollers keep the belt on track and prevent sagging.
- The driving unit: Motors with speed-reduction gears that power the belt and ensure smooth operation.
- The pulleys: Positioned to control the belt’s movement, drive, redirect, turn, tension, and track the belt.
- The clamping straps: Hold down fixtures and components.
- Add-on modules: Additional parts for reinforcement, including stands and lateral guides.
Conveyor belts can be made from rubber, metal, leather, fabric, or plastic. The material should be chosen based on the operating conditions to ensure suitable thickness and strength.

Functions of the conveyor belt
A conveyor belt’s primary function is transporting materials from Point A to Point B with minimal effort. The pace, direction, curvature, and size of a conveyor belt can vary depending on the user’s needs. In many industries, a conveyor belt moves products through a manufacturing or packaging line and then back out.
Conveyor belts usually fall into two categories: lightweight and heavyweight.
Lightweight belting Lightweight belting is designed to meet various material handling requirements across diverse industries. It has a working tension of less than 160 pounds per inch of width. The four main types of light-duty conveyor belts are:
- Solid plastic: Durable and easy to clean, making it ideal for food processing where hygiene is crucial.
- Non-woven: Offers flexibility and cushioning, suitable for handling delicate items like pharmaceuticals.
- Thermoplastic covered: Resistant to chemicals and wear, perfect for unit package handling where consistency is needed.
- Lightweight rubber: Provides good grip and durability, making it useful in the paper goods industry where reliability is key.
Industries that benefit from lightweight belting include:
- Food processing: Lightweight belts are hygienic and easy to clean, ensuring food safety.
- Unit package handling: Provides consistent movement and handling of packages with minimal damage.
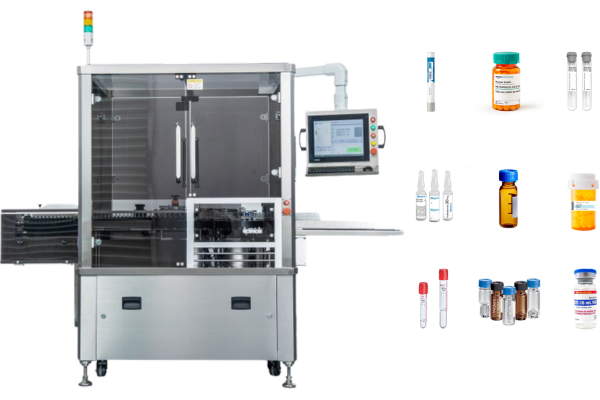
- Pharmaceutical: Ensures gentle handling of delicate products, reducing the risk of breakage. Most of our pharmaceutical labeling machines use lightweight conveyor belts, which is one of the reasons for the low wastage of our labeled products. Many of our labeling solutions (e.g.ampoule labeling solutions and syringe labeling solutions) specify the use of lightweight belts for added peace of mind.
- Paper goods: Durable and reliable, suitable for continuous operation and high-volume handling.
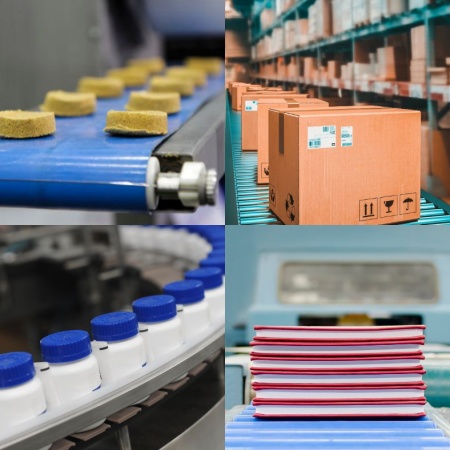

- Heavyweight belting: Heavyweight conveyor belting has a tension of at least 160 pounds per inch of width and is used for applications requiring continuous movement of bulky, heavy materials. Often coated with PTFE, these belts can withstand high temperatures.
Industries that use heavyweight belting include:
- Mining: Heavy-duty belts can handle the continuous movement of heavy, abrasive materials.
- Manufacturing: Suitable for transporting large, bulky items efficiently.
- Waste/recycling: Strong and durable, ideal for handling diverse and heavy waste materials.
- High-temperature food processing: PTFE-coated belts withstand high temperatures, ensuring safe and efficient food processing.
By selecting the appropriate type of conveyor belt, industries can improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and maintain high standards of product handling and transportation.
Uses and applications of conveyor belts
Conveyor belts serve a wide range of uses and applications across various settings and industries, whether lightweight or heavyweight. These systems significantly impact efficiency, productivity, and labor.
Uses and advantages of conveyor belts
A conveyor system serves a wide variety of uses, such as:
- Quickly and reliably transport large amounts of material.
- Stacking materials at the end of a transportation line for easy collection.
- Streamlining the process of moving items from Point A to Point B efficiently.
- Moving products vertically or horizontally with great flexibility.
Belt conveying systems are evolving with technology to meet the specific needs of modern operations, particularly through the integration of robotics and automation.
The advantages of using a conveyor belt system include:
- Reducing labor: By automating the transport process, businesses can decrease the need for manual labor, leading to higher productivity and time efficiency.
- Protecting workers: Conveyor belts minimize the risk of injuries from carrying heavy loads, making workplaces safer.
- Preventing product damage: During transportation, conveyor belts ensure that products are handled gently and securely, reducing the risk of damage.
- Flexible routing: Products can be easily transferred onto different routes, allowing for a high degree of flexibility in operations.
- Simple maintenance: Conveyor belt systems are durable and long-lasting, with relatively simple maintenance requirements, ensuring continuous operation without frequent downtime.

Applications of conveyor belts
Conveyor systems are utilized in numerous industries, including air travel, mining, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Motorized conveyor belts are traditional forms of conveying systems that actively transport materials, contrasting with roller-based systems that do not utilize motors.
Air travel
At airports, conveyor belts are essential for efficiently processing, sorting, loading, and unloading passenger luggage. The baggage carousel is a common application, where luggage is loaded onto the belt in a secure area and swiftly delivered to the terminal. A flat belt conveyor is commonly used in baggage handling systems to ensure the efficient movement of luggage. The belt continuously circulates, ensuring efficient delivery and easy access for passengers.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, conveyor belt systems are used to transport cardboard boxes or pallets full of medical supplies before and after packaging and distribution. These systems ensure that products are moved efficiently and safely through various stages of production and shipping.
Manufacturing and mining
In manufacturing and mining, conveyor belts transport vast amounts of material through tunnels, along roads, and up steep slopes. These industries require durable belting material and robust support rollers to handle heavy loads and harsh conditions.
Hinged steel belts are specifically designed for transporting heavy and hot parts from forging machines to various storage locations.
Food processing
In food processing, conveyor belts are crucial in the product lifecycle. Items are spread, stamped, rolled, glazed, fried, sliced, and powdered—all while moving on the belt. Plastic belts are commonly used in automated assembly operations to meet the demands of efficiency and speed in material movement. Conveyor belts save countless hours of manual labor, allowing goods to be processed in mass quantities while maintaining high quality. Products move seamlessly from start to finish, ensuring uniformity and efficiency.
Industry-specific requirements
Each industry has specific requirements for the type of conveyor belt they use. From shipyards and power plants to bakeries and ice cream plants, conveyor belts are favored for their simplicity and reliability. They are designed to meet the unique demands of each application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Conveyor belts are vital in many industries, enhancing efficiency and safety. By understanding “how do conveyor belts work,” businesses can select the right type for their needs, improving productivity and reducing costs. Their reliability and flexibility make them indispensable in modern industrial processes.
References and citations
FAQS
How do you maintain a conveyor belt system?
Regular maintenance of a conveyor belt system involves checking for wear and tear, ensuring proper tension, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting the belt for damage. Periodic cleaning and timely replacement of worn-out components are also essential to keep the system running smoothly.
Can conveyor belts be customized for specific industries?
Yes, conveyor belts can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries. Customization options include belt material, width, length, speed, and the addition of support rollers or other features to enhance performance in particular applications.
What are the safety considerations when using conveyor belts?
Safety considerations include installing emergency stop buttons, ensuring proper guarding around moving parts, training employees on safe operation, and conducting regular safety inspections. It is also important to keep the area around the conveyor belt free from obstructions to prevent accidents.