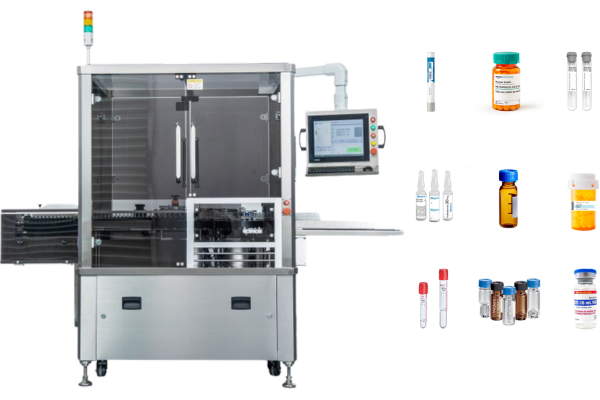
In today’s automated world, CCD vision detection plays a pivotal role in the advancement of industrial precision and efficiency.
These systems utilize Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) image sensor technology to convert light into electronic signals, offering superior image quality that is crucial for intricate inspection and control tasks in various industries.
The fundamentals of CCD sensor technology
- Definition and mechanism: CCD sensors are semiconductor devices that capture light and convert it into electronic signals. The technology is highly appreciated for its high resolution and sensitivity, which are essential for capturing detailed images in low-light conditions. The CCD sensor’s strengths in producing high-quality, low-noise images make it preferable for applications like medical imaging and astrophotography.
- Comparison with CMOS sensors: Unlike CMOS sensors that convert photo charge into a voltage at the pixel site, CCDs transfer the charge to a common output structure that converts the charge into a voltage, resulting in higher quality images with less noise. CMOS stands for complementary metal oxide semiconductor. Advancements in CMOS sensor technology, particularly in dynamic range and quantum efficiency, make them increasingly competitive with CCD sensors in various applications, such as astronomy and machine vision.
Key components and functions
- CCD cameras: These are the primary devices used in vision recognition systems for capturing images. They convert light into electronic signals, enabling high-quality image capture.

- Illumination systems: Proper lighting is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of CCD cameras, often involving specialized lights to enhance image clarity and contrast.
- Image acquisition hardware: This includes frame grabbers and digitizers that convert analog video signals from the CCD camera into digital form for processing.
- Processing software: Advanced algorithms analyze digital images to detect, identify, and measure various characteristics for quality control purposes.

Performance metrics of CCD machine vision systems
- Resolution: Refers to the amount of detail the camera can capture, crucial for applications requiring fine detail identification.
- Sensitivity: Determines how effectively the camera can capture images under low light conditions. CCD cameras are known for their high light sensitivity, making them ideal for applications requiring detailed imaging. However, advancements in CMOS technology have significantly improved their low-light sensitivity, enabling them to compete effectively in fields such as astronomy and surveillance.
- Frame rate: The speed at which images are captured and processed, is important in high-speed production lines.
- Signal-to-noise ratio: A measure of the clarity of the image data captured, with higher ratios indicating clearer images.
Applications across industries
- Manufacturing automation: CCD systems check for defects, ensure alignment, and verify assembly completeness in automated production lines. They play a crucial role in machine vision inspection, providing high-quality image analysis for precise visual assessments.
- Electronics assembly: Used to inspect the placement and soldering of components on circuit boards.
- Packaging industry: Ensures that packaging is correctly sealed and labeled before shipment.
- Automotive quality control: Checks components and assemblies for defects to ensure reliability and safety.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Monitors packaging and labeling to comply with stringent health regulations. Our labeling pharma labeling machines, like vial labeling machines and syringe labeling machines, are equipped with the system in the production line.

Integration and case studies
- Precise positioning and defect detection: Systems are tailored to identify minute imperfections, enhancing product quality in machine vision applications.
- A case study in high-speed production: Illustration of a CCD system integrated into a beverage bottling line to inspect bottle caps at high speeds.
Technical challenges and solutions for image quality
- Complexity in system integration: Strategies to seamlessly integrate CCD systems with existing industrial automation environments.
- Handling high-speed data: Addressing the challenge of processing large volumes of data in real-time with advanced computing solutions. Additionally, the competition from CMOS cameras, which are increasingly adopted due to their compact size and low power consumption, is notable. Modern CMOS cameras are closing the gap in performance with CCD sensors, especially in high-speed motion imaging.
- Stability in harsh environments: Enhancing the durability of CCD cameras to withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations.
Recent developments and future trends in CCD and CMOS sensors
- Advancements in AI and machine learning: Incorporating intelligent algorithms to improve decision-making processes based on image data. Additionally, advancements in CMOS image sensors have made them increasingly viable for medical and scientific imaging, impacting the future of CCD vision systems.
- Potential future directions: Innovations that could expand the capabilities of CCD vision systems, such as integration with robotic systems for adaptive manufacturing.
Conclusion
CCD vision detection have become an indispensable tools in modern manufacturing and quality control processes. With their unmatched ability to capture high-quality images, these systems provide the critical visual inputs needed for precise, automated decision-making.
As technology progresses, integrating CCD systems with emerging technologies like AI is expected to revolutionize industries further, making processes more efficient, reliable, and adaptable to changing market needs. The continued evolution of CCD technology will undoubtedly play a central role in the future of industrial automation.