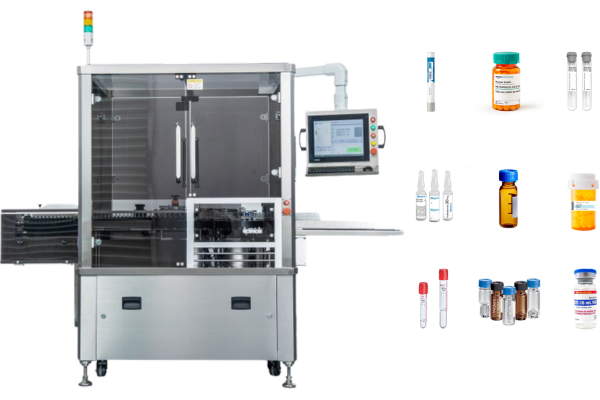
In the realm of medical equipment, auto-injection device labeling is essential for ensuring both safety and compliance. This guide will walk you through the nuances of labeling various types of auto-injectors, detailing the specific areas of application, standards, and emerging technologies.
Understanding these elements is crucial for manufacturers and healthcare providers who depend on the accuracy and reliability of these labels.
Types of auto-injection devices
- Pre-filled syringes: Often used in hospitals and clinics for vaccines and other injectables. Labels must contain drug information and dosage.
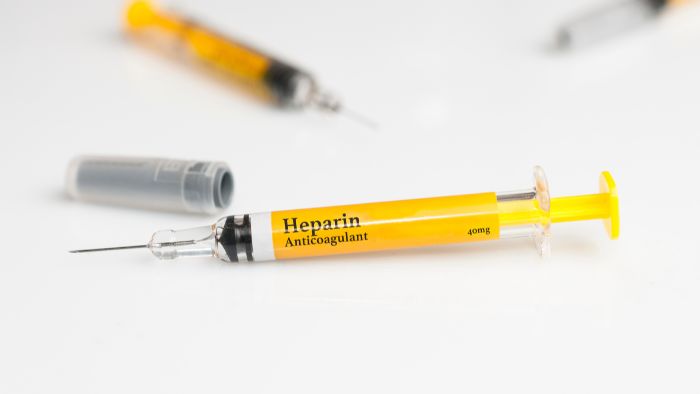
- Auto-injector pens: Commonly used for self-administration of medications like insulin or epinephrine. Labels should include usage instructions and expiration dates.
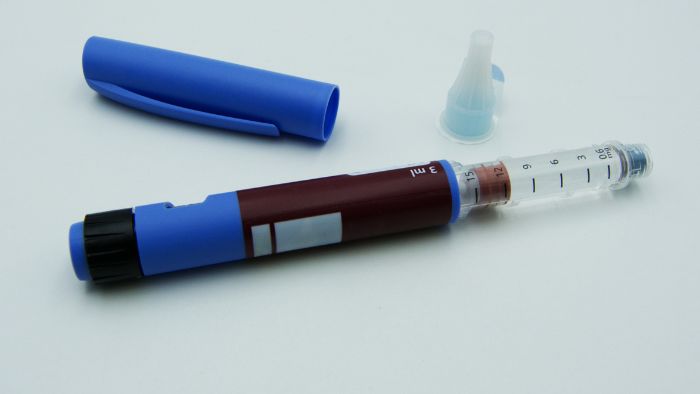
- Disposable auto-injectors: Designed for one-time use with emergency medication. Labeling here focuses on clear, quick-read instructions due to the urgent nature of their use. The importance of packaging in these devices cannot be overstated, as it ensures safety, usability, and proper handling.
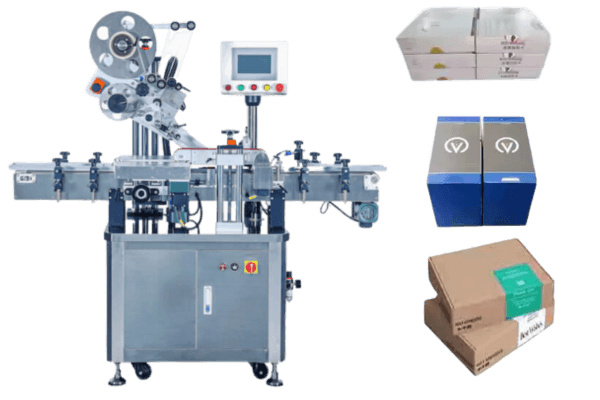
Labeling solutions, locations, and requirements
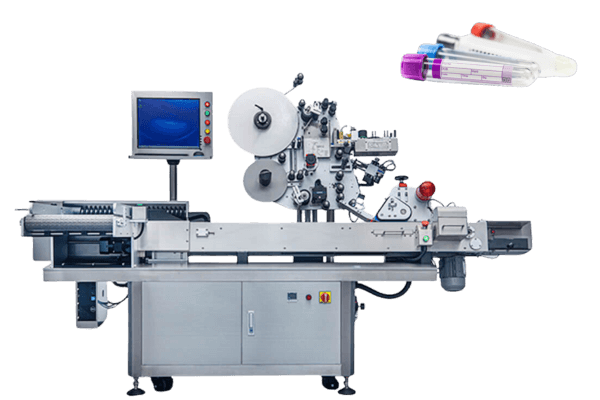
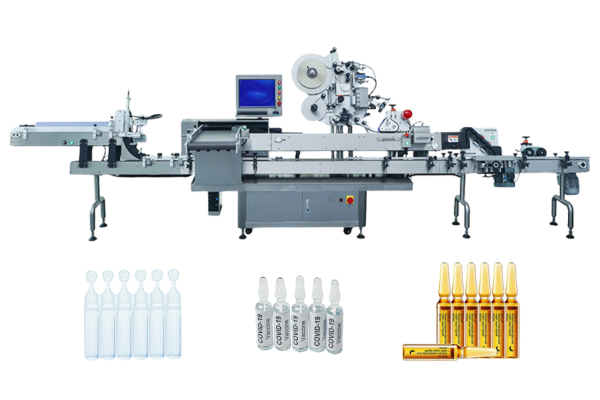
- Syringe body: The main cylinder of a syringe where labels must resist wear and chemical exposure. We offer labeling solutions for auto-injector bodies with high precision and speed, incorporating laser coding technology to ensure label precision and durability.
- Cap: Small area requiring high-precision labels that often hold critical warnings and allergy information.
- Plunger: The end of the syringe may have instructional labels to guide the user through the proper medication administration steps.
Operational procedures and standards
- Setting up Labeling Machines: Proper installation and calibration to ensure label accuracy and adherence.Setting up a dedicated production line for labeling auto-injectors is crucial to handling device-specific requirements efficiently and ensuring optimal performance.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Creating detailed guides for each labeling step to maintain consistency.
- Quality Control Checks: Regular inspections and tests to verify label placement, readability, and adherence.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
- Common issues: Addressing label misalignment, smearing, and adhesion failures.
- Routine maintenance: Scheduled checks and replacements of key machine components like sensors and rollers.
- Calibration for precision: Techniques to ensure ongoing accuracy in label application, crucial for regulatory compliance.
Regulatory compliance and standards in the pharmaceutical industry
- Industry regulations: Adherence to standards like ISO and specific FDA guidelines for pharmaceutical labeling.
- Compliance of label content: Providing a tailored solution to ensure that all mandatory information is present, accurate, and easily legible to meet safety standards.
Technological innovations and future trends
- Advanced labeling technologies: Incorporation of smart sensors and vision systems to improve label placement and quality control. NFC technology in smart packaging for auto-injectors enables manufacturers to track the location of auto-injectors throughout the supply chain, enhancing safety and reducing counterfeiting risks, while ensuring proper storage and transportation conditions.
- Automation and data integration: Leveraging data analytics for predictive maintenance and increased operational efficiency. Smart packaging enhances supply chain management for auto-injectors by using RFID and NFC technology to track the location of products throughout the entire supply chain, helping prevent counterfeiting and ensuring proper storage and transportation conditions.
- Future directions: Exploring biodegradable labels and RFID tagging to enhance patient safety and tracking.
Conclusion
Throughout the medical industry, the role of auto-injection device labeling cannot be overstated. With advances in technology and increased regulatory scrutiny, the process of labeling these devices has become more complex and vital.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the necessary procedures, standards, and innovations in the field of auto-injection device labeling, ensuring that industry professionals are equipped to meet the current and future demands of healthcare delivery.