In the realm of pharmaceutical manufacturing, adherence to GMP standards is not merely a regulatory requirement but a cornerstone of ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of medicinal products.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards encompass a set of guidelines and principles that govern the production, testing, and quality assurance of pharmaceuticals and medical devices. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) regulations established by the FDA outline essential systems for the design, monitoring, and control of manufacturing processes, ensuring the overall quality assurance in drug production.
These standards are meticulously designed to mitigate risks inherent in manufacturing processes and to uphold stringent quality control measures throughout the product lifecycle.
Good Manufacturing Practice’s basic principles
At its core, GMP revolves around several fundamental principles that underpin its application across various aspects of pharmaceutical production. First and foremost is the meticulous control and management of raw materials used in manufacturing processes. This entails stringent testing, validation, and documentation to ensure that only materials of approved quality are utilized.
Secondly, GMP emphasizes the robust control of manufacturing processes themselves. This includes the calibration and maintenance of equipment, the monitoring of environmental conditions, and the implementation of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) to minimize variability and ensure consistency in product output. These measures ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled, maintaining high standards of safety and quality.
Furthermore, GMP places significant emphasis on the management and training of personnel involved in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Adequate training ensures that staff are proficient in GMP principles, thereby fostering a culture of compliance and accountability within the workforce. Personal hygiene is also critical in minimizing risks and ensuring the quality of the finished products.

Another critical aspect of GMP is the meticulous documentation of every aspect of production, from raw material procurement to final product distribution. Accurate and detailed records not only facilitate traceability and accountability but also serve as crucial evidence of compliance during regulatory inspections.
GMP application scope in the pharmaceutical industry
The application of GMP standards extends across a broad spectrum within the pharmaceutical industry. It governs the production of various types of pharmaceuticals, including small-molecule drugs, biologics, vaccines, sterile products, and drug products. Ensuring the quality and safety of drug products under CGMP regulations is crucial for maintaining their integrity, identity, strength, quality, and purity. Each category of pharmaceuticals may have specific GMP requirements tailored to its unique manufacturing processes and risks.
Moreover, GMP principles are not confined solely to pharmaceutical manufacturing but also extend to the production of medical devices. Manufacturers of medical devices must adhere to GMP guidelines to ensure the safety, reliability, and effectiveness of their products.
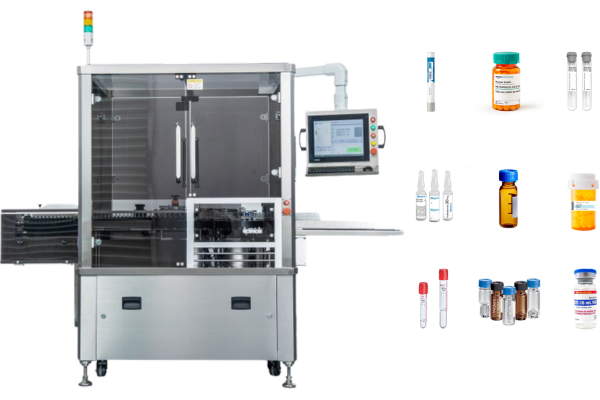
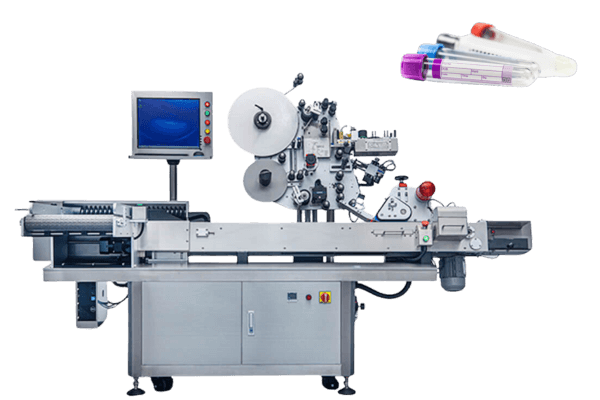
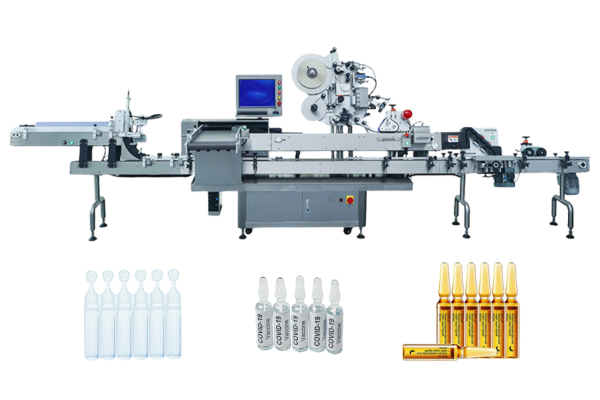
Viallabeller, as a manufacturer of pharmaceutical labeling machines, can provide GMP-compliant labeling services for pharmaceutical manufacturers, and we also have a range of labeling solutions for pharmaceutical containers, such as ampoules, syringes, vials ……
Implementation and oversight of quality assurance
Implementing GMP standards involves a systematic approach that begins with the development of comprehensive quality management systems (QMS). These systems outline the procedures and controls necessary to achieve and maintain GMP compliance throughout the manufacturing lifecycle, ensuring that all regulatory guidelines, including the minimum requirements, are met.
Furthermore, GMP compliance is subject to rigorous oversight by regulatory authorities and industry bodies. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and national health authorities enforce GMP through regular inspections and audits of pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities.

These inspections assess adherence to GMP guidelines, the quality of manufacturing processes, and the adequacy of documentation practices.
Global comparison of GMP guidelines
While the fundamental principles of GMP remain consistent globally, there are variations in how these standards are interpreted and implemented across different regions. For instance, the FDA’s GMP regulations in the United States emphasize risk-based approaches to quality management and require stringent documentation and validation practices. These regulations are often referred to as Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP), highlighting the importance of continuous improvement in manufacturing processes and risk management to prevent health risks and assure product quality.
In contrast, the EMA’s GMP guidelines in the European Union emphasize a holistic approach to quality assurance, focusing on continuous improvement, risk management, and the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Similarly, China’s State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA) has developed its own set of GMP regulations tailored to the specific needs of the Chinese pharmaceutical industry, with an emphasis on ensuring product quality and safety.
Impact of GMP standards
The impact of GMP standards on the pharmaceutical industry is profound and far-reaching. By setting rigorous quality standards and ensuring compliance through regulatory oversight, GMP ensures that pharmaceutical products are consistently produced, enhancing their reliability and consistency. This, in turn, instills confidence among healthcare professionals, patients, and regulatory authorities regarding the safety and efficacy of medicinal products.

Moreover, adherence to GMP standards facilitates global market access for pharmaceutical manufacturers by demonstrating their commitment to quality and compliance with international regulatory requirements. This is particularly crucial in a globalized pharmaceutical market where cross-border trade and regulatory harmonization play pivotal roles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GMP standards represent the gold standard in pharmaceutical manufacturing, encompassing principles and guidelines that ensure the highest levels of quality, safety, and efficacy in medicinal products. As pharmaceutical manufacturers navigate increasingly complex regulatory landscapes and technological advancements, adherence to GMP standards remains non-negotiable.
By upholding these standards, manufacturers not only safeguard public health but also contribute to the advancement of global healthcare standards. Thus, GMP standards continue to serve as the bedrock of pharmaceutical quality assurance, guiding industry practices and ensuring the delivery of safe and effective medicines worldwide.