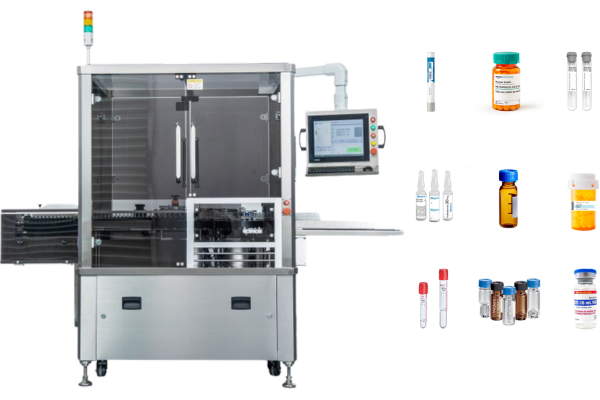
Pharma labeling is a crucial aspect of the pharmaceutical industry, serving as the primary communication channel between drug manufacturers and end-users. It provides essential information on drug identification, dosage, administration, and safety, which is collectively known as drug labeling.
Regulatory bodies around the world, such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, impose stringent requirements to ensure that every label on pharmaceutical products is accurate, informative, and compliant with local and international standards.
Global regulatory
- United States (FDA regulations): In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates comprehensive labeling to include the drug name, dosage form, net quantity, active ingredients, and the route of administration. The FDA also requires specific warnings, and the disclosure of adverse effects caused by drug interactions, particularly within the Recent Major Changes section, highlighting the critical nature of this information for patient safety and informed medical use. Furthermore, the labeling must be designed to meet readability standards to ensure that it is accessible to all users. The FDA imposes stringent regulations on pharmaceutical labeling, specifically for human prescription drugs, emphasizing the significance of compliance to ensure patient safety and avoid public health risks.
- European Union (EMA regulations): The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees labeling requirements in the EU, which include detailed instructions in all official languages of the European Union, depending on the countries where the drug is marketed. EMA guidelines focus on patient safety by requiring clarity in labeling, including explicit instructions on the use and potential side effects of the medication.
- China (NMPA regulations): The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) requires pharmaceutical labels in China to include both the generic and brand names of the drug, comprehensive dosage information, and manufacturing details. Labels must be in Mandarin, and they must clearly state any special storage conditions and expiration dates to maintain product efficacy and safety.
- India (CDSCO regulations): The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in India emphasizes both the active pharmaceutical ingredient content and the manufacturer’s details on the drug labels. Labels must provide detailed dosage instructions, contraindications, and the legal category of the drug (e.g., prescription-only or over-the-counter). It is crucial to include clear and comprehensive information on drug packaging and inserts for prescription drugs to prevent public health risks.
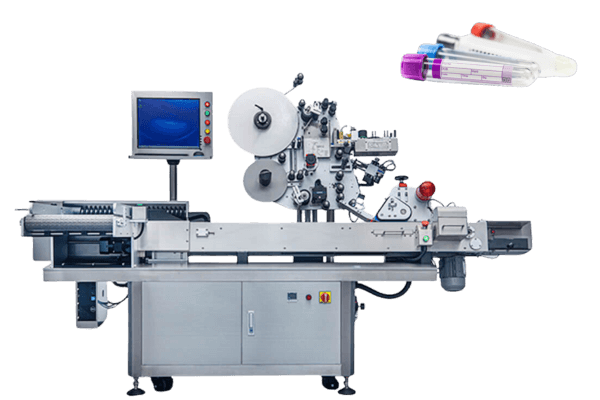
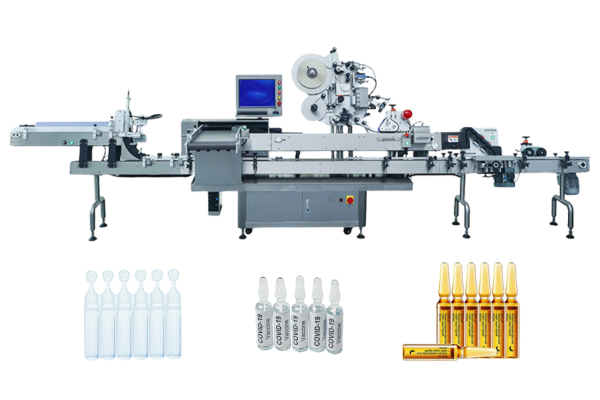
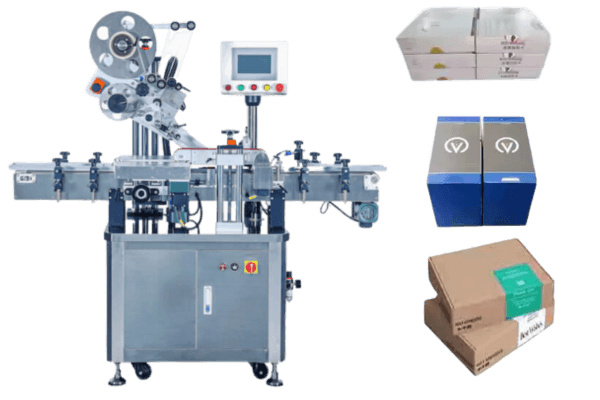
Our labeling machines meet all of these criteria and have a range of solutions, like vial labeling solution and syringe labeling solution, etc.
Key elements of pharmaceutical labeling regulations
Labeling regulations in the pharmaceutical sector are primarily aimed at ensuring patient safety and facilitating the proper use of medications. Important elements include:
- Drug identification: Clear identification of the drug, including its generic and brand names. It is crucial to include the National Drug Code (NDC) on pharmaceutical packaging to ensure FDA compliance and easy identification.
- Dosage information: Detailed instructions on dosage, administration methods, and frequency.
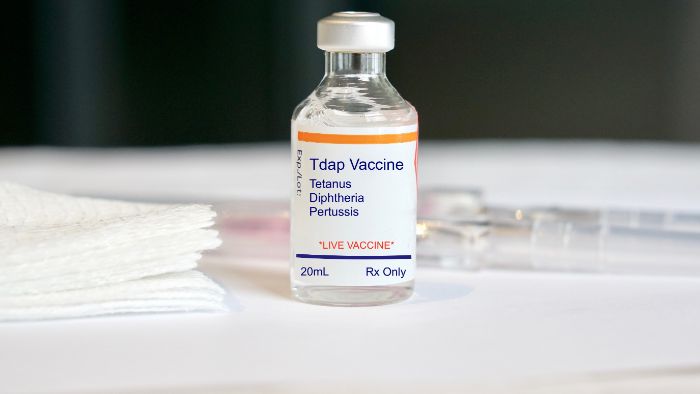
- Manufacturing and expiry dates: Essential for determining the drug’s shelf life.
- Ingredient listing: All active and inactive ingredients must be listed to inform users of potential allergens or chemical sensitivities.

Usage instructions and warnings: Comprehensive guidelines on how to use the medication, including warnings and possible side effects to prevent misuse and inform about potential risks. Prescription drug labeling plays a critical role in preventing medication use errors and enhancing patient understanding, especially for populations with low health literacy.
Special prescription drug labeling requirements
Certain pharmaceuticals require additional labeling considerations:
- Controlled substances: Additional security features like tamper-evident designs and traceability measures. The stringent labeling requirements set forth by the FDA for drug products emphasize the importance of clear and accurate information on pharmaceutical packaging.
- Orphan drugs and emergency use authorization: Special labeling that addresses the unique aspects of these drugs, including expanded access and compassionate use instructions. FDA-approved labeling is also crucial for various products, including toiletries and hand sanitizers, to ensure compliance with FDA regulations.
Sustainability and environmental regulations for pharmaceutical products
The shift towards sustainable practices has also impacted pharmaceutical labeling:
- Eco-friendly materials: Encouraging the use of recycled or biodegradable materials for pharmaceutical labels.
- Recycling and waste management: Labels must provide information on the proper disposal and recycling of pharmaceutical packaging.
Regulatory compliance and FDA approved labeling processes
Pharmaceutical companies must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to achieve label compliance:
- Label design submission: Labels must be submitted to regulatory authorities for approval before a drug can be marketed. The importance of drug product packaging in relation to regulatory guidelines established by the FDA cannot be overstated, as these regulations improve the legibility and standardization of labeling information.
- Label modification and re-approval: Any changes to the labeling require re-submission and approval, ensuring that all information remains current and compliant.
Technology’s role in compliance
Advancements in technology facilitate compliance with labeling regulations:
- Automated labeling systems: Improve accuracy and efficiency in label applications.
- Label management software: Helps manage label design, modifications, and compliance documentation.
Conclusion
Pharma labeling is not just a regulatory requirement but a vital tool for ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. By adhering to the guidelines set by various global regulatory bodies, manufacturers can ensure that their products are used safely and effectively.
The continuous evolution of labeling standards demands ongoing vigilance and adaptation from all stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry to uphold the standards of patient care and safety.