Syringe manufacturing is a critical process that demands the highest level of hygiene and precision to ensure the safety and efficacy of these essential medical tools.
As medical devices that are essential for the administration of drugs, vaccines, and other substances directly into the body, syringes must be produced under stringent health standards. These regulations are designed to prevent contamination and ensure that every syringe produced meets the required safety norms.
This article outlines the vital health standards and practices involved in the manufacturing of syringes, emphasizing the importance of materials, production environment, sterilization, and quality control.
Basic requirements in plastic syringe production
The production of syringes involves several basic but crucial requirements that ensure the products are safe for medical use:
- Material Selection: All materials used in syringe production must be non-toxic, biocompatible, and suitable for sterilization. This includes the plastic for the body and plunger, the rubber for the gasket, and any lubricants used.
- Injection Molding: Injection molding is essential in producing quality syringes, ensuring optimal functionality and compliance with health standards.
- Production Equipment: Equipment must be regularly sterilized and maintained to prevent any risk of contamination.
- Manufacturing Environment: The production area must comply with cleanroom standards, which are critical to maintaining an environment free from airborne particles.
Key hygiene controls in medical device production processes
Ensuring cleanliness and hygiene throughout the production process is non-negotiable in syringe manufacturing:
- Raw Material Handling: Storage and handling of raw materials must prevent their contamination. This includes sealed packaging and controlled storage environments.
- Processing Stages: During the syringe manufacturing process, strict hygiene controls are essential, especially when parts are being formed and assembled. Hygiene considerations differ between plastic syringes and glass syringes, with each material requiring specific handling and sterilization protocols.
- Assembly and Packaging: Syringes are assembled and packaged in sterile conditions. The packaging itself must also be sterile, often achieved through radiation sterilization or ethylene oxide sterilization.
Sterilization and disinfection standards
Sterilization is crucial in syringe manufacturing, ensuring that the final products are free from all microorganisms:
- Sterilization techniques: Common sterilization methods include gamma radiation, steam sterilization, and ethylene oxide. Each method has its specific applications and effectiveness.
- Choice and use of disinfectants: The appropriate disinfectants for different stages of the production process are selected based on their effectiveness and compatibility with the materials.
Pharmaceutical packaging plays a vital role in maintaining sterility, ensuring that medical treatments are delivered safely and effectively.
Quality control and inspection
Maintaining high standards through rigorous quality control and inspection is vital:
- Internal quality control: This involves continuous monitoring of the production processes, regular auditing, and testing.
- Product testing: Finished syringes undergo several tests, including sterility testing, leak testing, and functionality testing. It is important to inspect the syringe barrel for quality to ensure a leak-proof seal and accurate dosing.
- Traceability systems: Each batch of syringes is traceable back to its production data, which is crucial for quality assurance and addressing any issues post-production.
Regulations and certification in pharmaceutical packaging
Compliance with national and international regulations is mandatory for syringe manufacturers:
- Overview of regulations: Different countries have varying regulations governing the production of medical devices. In the U.S., syringes are regulated by the FDA, while in Europe, they must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Cardinal Health is an example of a company that complies with these syringe manufacturing regulations.
- Certification processes: Obtaining certifications like ISO 13485 for medical devices is essential for syringe manufacturers to enter global markets.
Employee training and continuous improvement in the healthcare sector
Ongoing employee training and continuous improvement are fundamental for maintaining high health standards:
- Employee training: Regular training in sterile manufacturing processes, personal hygiene, and handling protocols is mandatory. Training is also crucial for healthcare professionals who use these syringes to ensure they are well-equipped to address clinical challenges.
- Continuous improvement: Manufacturers must continuously seek improvements in technology and processes to enhance hygiene standards and efficiency.
Conclusion
In syringe manufacturing, maintaining stringent health standards is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical responsibility to ensure the safety and reliability of medical devices. As this sector evolves, so too must the processes and standards that govern it.
The significance of adhering to high manufacturing standards in the healthcare sector cannot be overstated, as syringes have various medical applications, including surgeries, sterilization, and wound care.
Innovations in materials, production methods, and sterilization techniques will continue to improve the quality and safety of syringes. However, the core emphasis on hygiene, rigorous quality control, and compliance with global standards remains pivotal in syringe manufacturing.
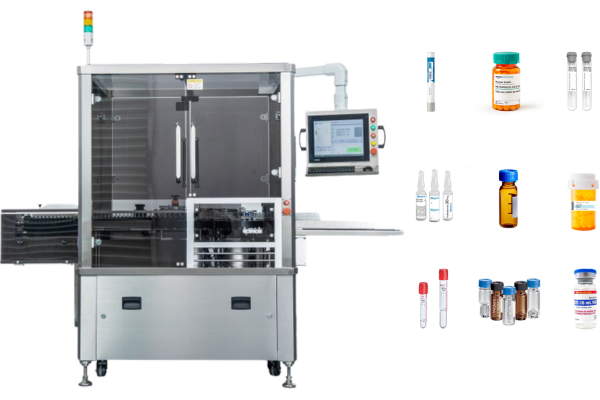
However, syringe labeling is an important part of manufacturing. Vialabeller can provide syringe labeling machines for pharmaceutical companies and help them get their products to market quickly.
We give labeling machines for the following pharma devices: